New Publication in ACS Chem. Biol.
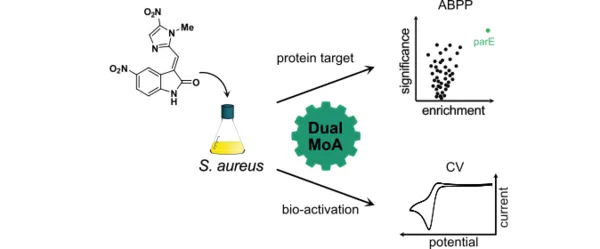
Nitroimidazoles such as metronidazole are used as anti-infective drugs against anaerobic bacteria. Upon in vivo reduction of the nitro group, reactive radicals damage DNA and proteins in the absence of oxygen. Unexpectedly, a recent study of nitroimidazoles linked to an indolin-2-one substituent revealed potent activities against aerobic bacteria. This suggests a different, yet undiscovered mode of action (MoA). To decipher this MoA, we first performed whole proteome analysis of compound-treated cells, revealing an upregulation of bacteriophage-associated proteins, indicative of DNA damage. Since DNA binding of the compound was not observed, we applied activity-based protein profiling (ABPP) for direct target discovery. Labeling studies revealed topoisomerase IV, an essential enzyme for DNA replication, as the most enriched hit in pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus cells. Subsequent topoisomerase assays confirmed the inhibition of DNA decatenation in the presence of indolin-2-one nitroimidazole with an activity comparable to ciprofloxacin, a known inhibitor of this enzyme. Furthermore, we determined significantly increased redox potentials of indolin-2-one nitroimidazoles compared to classic 5-nitroimidazoles such as metronidazole, which facilitates in vivo reduction. Overall, this study unravels that indolin-2-one-functionalized nitroimidazoles feature an unexpected dual MoA: first, the direct inhibition of the topoisomerase IV and second the classic nitroimidazole MoA of reductive bioactivation leading to damaging reactive species. Importantly, this dual MoA impairs resistance development. Given the clinical application of this compound class, the new mechanism could be a starting point to mitigate resistance.
Reinhardt, T., Lee, K.M., Niederegger, L., Hess, C.R., Sieber, S.A., "Indolin-2-one Nitroimidazole Antibiotics Exhibit an Unexpected Dual Mode of Action", ACS Chem. Biol.
Link: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.2c00462
Copyright American Chemical Society. Reproduced with permission.