New Publication in Angewandte Chemie Int. Ed.
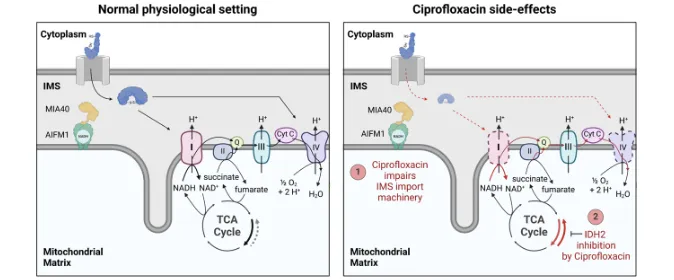
Fluoroquinolones (FQs) are an important class of potent broad-spectrum antibiotics.However, their general use is more and more limited by adverse side effects. While general mechanisms for the fluoroquinolone-associated disability (FQAD) have been identified, theunderlying molecular targets of toxicity remain elusive. In this study, focusing on the most commonly prescribed FQs Ciprofloxacin and Levofloxacin, whole proteome analyses revealedprominent mitochondrial dysfunction in human cells, specifically of the complexes I and IV ofthe electron transport chain (ETC). Furthermore, global untargeted chemo-proteomic methodologies such as photo-affinity profiling with FQ-derived probes, as well as derivatization-free thermal proteome profiling, were applied to elucidate human protein off-targets of FQs in living cells. Accordingly, the interactions of FQs with mitochondrial AIFM1and IDH2 have been identified and biochemically validated for their contribution tomitochondrial dysfunction. Of note, the FQ induced ETC dysfunction via AIFM1 activates the reverse carboxylation pathway of IDH2 for rescue, however, its simultaneous inhibition further enhances mitochondrial toxicity. This off-target discovery study provides unique insights into FQ toxicity enabling the utilization of identified molecular principles for thedesign of a safer FQ generation.
Reinhardt, T., El Harraoui, Y., Rothemann, A., Jauch, A. T., Müller-Deubert, S., Köllen, M. F., Risch, T., Jacobs, L. H. C., Müller, R., Traube, F. R., Docheva, D., Zahler, S., Riemer, J. & Bach, N. C., Sieber, S. A. “Chemical proteomics reveal human off-targets of fluoroquinolone induced mitochondrial toxicity”, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.
Link: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202421424
This reprint is liscensed under CC BY 4.0