PET of CXCR4 expression by a (68)Ga-labeled highly specific targeted contrast agent
Gourni E, Demmer O, Schottelius M, D'Alessandria C, Schulz S, Dijkgraaf I, Schumacher U, Schwaiger M, Kessler H, Wester HJ
01.11.2012 [Original Artikel]
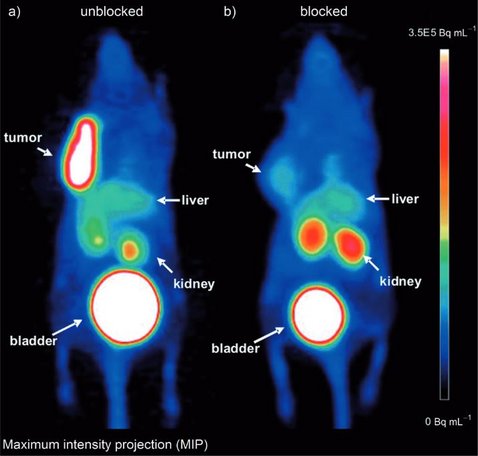
The overexpression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 plays an important role in oncology, since together with its endogenous ligand, the stromal cell-derived factor (SDF1-α), CXCR4 is involved in tumor development, growth, and organ-specific metastasis. As part of our ongoing efforts to develop highly specific CXCR4-targeted imaging probes and with the aim to assess the suitability of this ligand for first proof-of-concept studies in humans, we further evaluated the new (68)Ga-labeled high-affinity cyclic CXCR4 ligand, (68)Ga-CPCR4-2 (cyclo(D-Tyr(1)-[NMe]-D-Orn(2)-[4-(aminomethyl) benzoic acid,(68)Ga-DOTA]-Arg(3)-2-Nal(4)-Gly(5))). Additional biodistribution and competitions studies in vivo, dynamic PET studies, and investigations on the metabolic stability and plasma protein binding were performed in nude mice bearing metastasizing OH1 human small cell lung cancer xenografts. CXCR4 expression on OH1 tumor sections was determined by immunohistochemical staining. (nat)Ga-CPCR4-2 exhibits high CXCR4 affinity with a half maximum inhibitory concentration of 4.99 ± 0.72 nM. (68)Ga-CPCR4-2 showed high in vivo stability and high and specific tumor accumulation, which was reduced by approximately 80% in competition studies with AMD3100. High CXCR4 expression in tumors was confirmed by immunohistochemical staining. (68)Ga-CPCR4-2 showed low uptake in nontumor tissue and particularly low kidney accumulation despite predominant renal excretion, leading to high-contrast delineation of tumors in small-animal PET studies. The small and optimized cyclic peptide CPCR4-2 labeled with (68)Ga is a suitable tracer for targeting and imaging of human CXCR4 receptor expression in vivo. The high affinity for CXCR4, its in vivo stability, and the excellent pharmacokinetics recommend the further evaluation of (68)Ga-CPCR4-2 in a proof-of-concept study in humans.
A conformationally frozen peptoid boosts CXCR4 affinity and anti-HIV activity
Demmer O, Frank AO, Hagn F, Schottelius M, Marinelli L, Cosconati S, Brack-Werner R, Kremb S, Wester HJ, Kessler H
03.07.2012 [Original Artikel]
There can be only one: Using a peptoid motif obtained by shifting the arginine side chain of a pentapeptide previously developed by Fujii et al. to the neighboring nitrogen atom restricts the conformational freedom and yields a conformationally homogeneous peptide (see picture) with a 100-fold higher binding affinity to the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in the picomolar range. Its efficiency to inhibit HIV-1 infections is also demonstrated.
Design, synthesis, and functionalization of dimeric peptides targeting chemokine receptor CXCR4
Demmer O, Dijkgraaf I, Schumacher U, Marinelli L, Cosconati S, Gourni E, Wester HJ, Kessler H
12.09.2011 [Original Artikel]
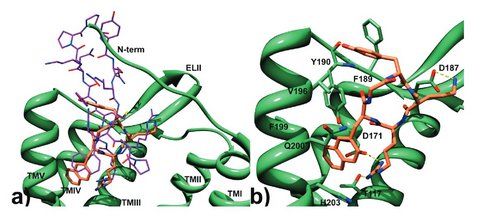
The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is a critical regulator of inflammation and immune surveillance, and it is specifically implicated in cancer metastasis and HIV-1 infection. On the basis of the observation that several of the known antagonists remarkably share a C(2) symmetry element, we constructed symmetric dimers with excellent antagonistic activity using a derivative of a cyclic pentapeptide as monomer. To optimize the binding affinity, we investigated the influence of the distance between the monomers and the pharmacophoric sites in the synthesized constructs. The affinity studies in combination with docking computations support a two-site binding model. In a final step, 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA) was introduced as chelator for (radio-)metals, thus allowing to exploit these compounds as a new group of CXCR4-binding peptidic probes for molecular imaging and endoradiotherapeutic purposes. Both the DOTA conjugates and some of their corresponding metal complexes retain good CXCR4 affinity, and one (68)Ga labeled compound was studied as PET tracer.
PET imaging of CXCR4 receptors in cancer by a new optimized ligand
Demmer O, Gourni E, Schumacher U, Kessler H, Wester HJ
20.07.2011 [Original Artikel]
The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is a critical regulator of inflammation and immune surveillance, and it is specifically implicated in cancer metastasis and HIV-1 infection. On the basis of the observation that several of the known antagonists remarkably share a C(2) symmetry element, we constructed symmetric dimers with excellent antagonistic activity using a derivative of a cyclic pentapeptide as monomer. To optimize the binding affinity, we investigated the influence of the distance between the monomers and the pharmacophoric sites in the synthesized constructs. The affinity studies in combination with docking computations support a two-site binding model. In a final step, 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA) was introduced as chelator for (radio-)metals, thus allowing to exploit these compounds as a new group of CXCR4-binding peptidic probes for molecular imaging and endoradiotherapeutic purposes. Both the DOTA conjugates and some of their corresponding metal complexes retain good CXCR4 affinity, and one (68)Ga labeled compound was studied as PET tracer.
Introduction of functional groups into peptides via N-alkylation
Demmer O, Dijkgraaf I, Schottelius M, Wester HJ, Kessler H
12.04.2008 [Original Artikel]
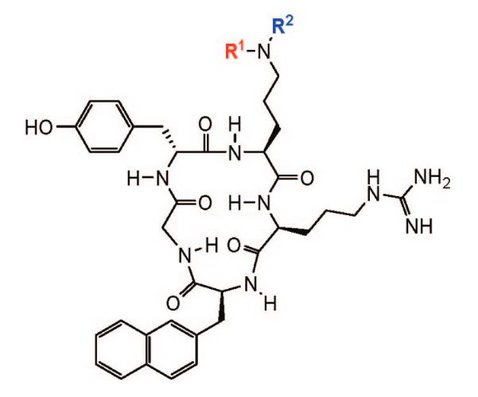
An optimized protocol for the mild and selective Fukuyama-Mitsunobu reaction was used for mono- and di- N-alkylation on solid support. Thereby, nonfunctionalized aliphatic and aromatic residues are quickly introduced into transiently protected, primary amines of a linear peptide. N-Alkylation can also be used to implement alkyl chains carrying (protected) functionalities suited for subsequent modification. Applicability of this method is demonstrated by various N-alkylated analogues of a cyclic CXCR4 receptor antagonist originally developed by Fujii et. al.