Wolfgang Kuttenlochner
My doctoral thesis focused on two important proteases, the proteasome and the caseinolytic protease P (ClpP). They are involved in a myriad of biological processes, and dysregulation or malfunction of these proteases is associated with various pathological disorders, including autoimmunity, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases. Inhibition of these proteases by compounds derived from natural sources offers a promising strategy to develop new drugs due to their high target specificity and potency. Therefore, we aimed to explore the mechanisms by which different cyclic natural product classes, namely epoxyketones, syrbactins, β-lactones, and azetidomonamides, interact with the proteasome and ClpP. To elucidate their modes of action at atomic resolution and investigate their biosynthesis pathways, an integral approach using X-ray crystallography combined with biochemical methods, chemical synthesis, computational analysis, and the development and conduction of activity assays was applied. This thesis provided comprehensive rationales for the development of new proteasome inhibitors and revealed the mechanisms of various cyclic ClpP-modulating compounds. Furthermore, the characterization of enzymes involved in epoxomicin and β-lactone biosynthesis provided valuable insights into their mechanisms.
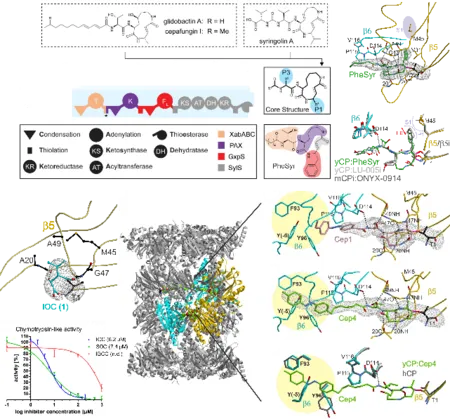
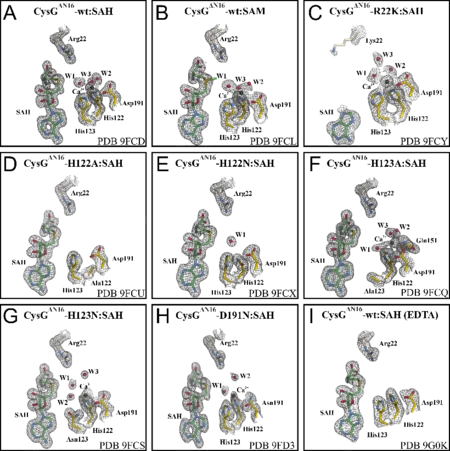
Crystal structures of the yeast 20S proteasome in complex with syrbactin-class inhibitors highlighted rationales to enhance immunoproteasome specificity or tune their activity by light. Moreover, a minimal β-lactone scaffold necessary for effective proteasome inhibition was identified by structural and functional analysis of a natural product and various derivatives. In addition, the modes of action of cystargolide A, as well as azetidomonamide A towards ClpP from different bacterial sources was depicted in crystallographic studies. Both depend on water exclusion from the active site caused by the specific architecture of the natural products. Moreover, the first structural characterization of an epoxyketone synthase identified catalytic residues and comparison in a synthetic study further enhanced our mechanistic understanding of the FAD-dependent decarboxylation-desaturation-epoxidation reaction sequence. Focusing on the cystargolide and belactosin biosynthesis pathways, the crystal structures of their O-methyltransferases suggested an unusual metal-dependency. This was validated by mutagenesis studies combined with activity assays and ligand docking calculations.

Thesis
W. Kuttenlochner (2024), Structural and Functional Studies on Cyclic Protease Inhibitors and their Biosynthesis
Publications
Präve, L.*, Kuttenlochner, W.*, Tabak, W., Langer, C., Kaiser, M., Groll, M., Bode, H. B.
Bioengineering of Syrbactin Megasynthetases for Immunoproteasome Inhibitor Production
Chem, 2024, 10, 3212-23
Kuttenlochner, W., Beller, P., Kaysser, L., Groll, M.
Deciphering the SAM- and Metal-Dependent Mechanism of O-Methyltransferases in Cystargolide and Belactosin Biosynthesis: A Structure-Activity Relationship Study
J. Biol. Chem., 2024, 300 (107646), 1-8
Bozhüyük, K.*, Präve, L.*, Kegler, C.*, Schenk, L.*, Kaiser, S., Schelhas, C., Shi, Y.-N., Kuttenlochner, W., Schreiber, M., Kandler, J., Alanjary, M., Mohiuddin, TM., Groll, M., Hochberg,G., Bode, H. B.
Evolution-inspired engineering of nonribosomal peptide synthetases
Science, 2024, 383 (eadg4320), 1-11
Illigmann, A.*, Vielberg, M.-T.*, Lakemeyer, M.*, Wolf, F., Dema, T., Stange, P., Kuttenlochner, W., Liebhart, E., Kulik, A., Staudt, N. D., Malik, I., Grond, S., Sieber, S. A., Kaysser,L., Groll, M., Brötz-Oesterhelt, H. Structure of Staphylococcus aureus ClpP Bound to the Covalent Active-Site Inhibitor Cystargolide A
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2024, 63 (e202314028), 1-10
Beller, P., Fink, P., Wolf, F., Männle, D., Helmle, I., Kuttenlochner, W., Unterfrauner, D., Engelbrecht, A., Staudt, N. D., Kulik, A., Groll, M., Gross, H., Kaysser, L.
Characterization of the cystargolide biosynthetic gene cluster and functional analysis of the methyltransferase CysG
J. Biol. Chem., 2024, 300 (105507), 1-9
Morstein, J.*, Amatuni, A.*, Shuster, A.*, Kuttenlochner, W.*, Ko, T., Abegg, D., Groll, M., Adibekian, A., Renata, H., Trauner, D. H.
Optical Control of Proteasomal Protein Degradation with a Photoswitchable Lipopeptide
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2024, 63 (e202314791)
Shi, Y.-M., Hirschmann, M., Shi, Y.-N., Ahmed, S., Abebew, D., Tobias, N. J., Grün, P., Crames, J. J., Pöschel, L., Kuttenlochner, W., Richter, C., Herrmann, J., Müller, R., Thanwisai, A., Pidot, S. J., Stinear, T. P., Groll, M., Kim, Y., Bode, H. B.
Global analysis of biosynthetic gene clusters reveals conserved and unique natural products in entomopathogenic nematode-symbiotic bacteria
Nat. Chem., 2022, 14, 701-12
Scherlach, K., Kuttenlochner, W., Scharf, D. H., Brakhage, A. A., Hertweck, C., Groll, M., Huber, E. M.
Structural and Mechanistic Insights into C-S Bond Formation in Gliotoxin
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 14188-94